V. I. Melnikov
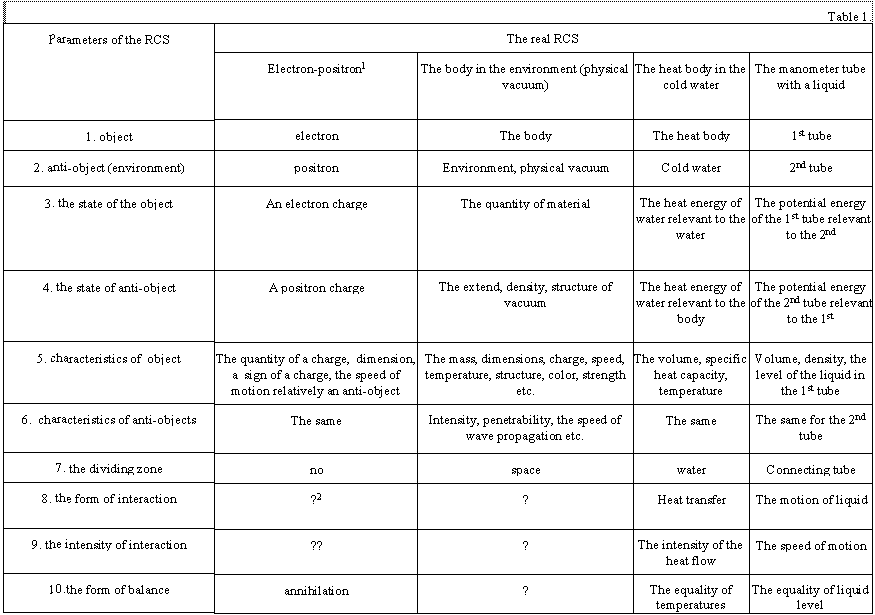
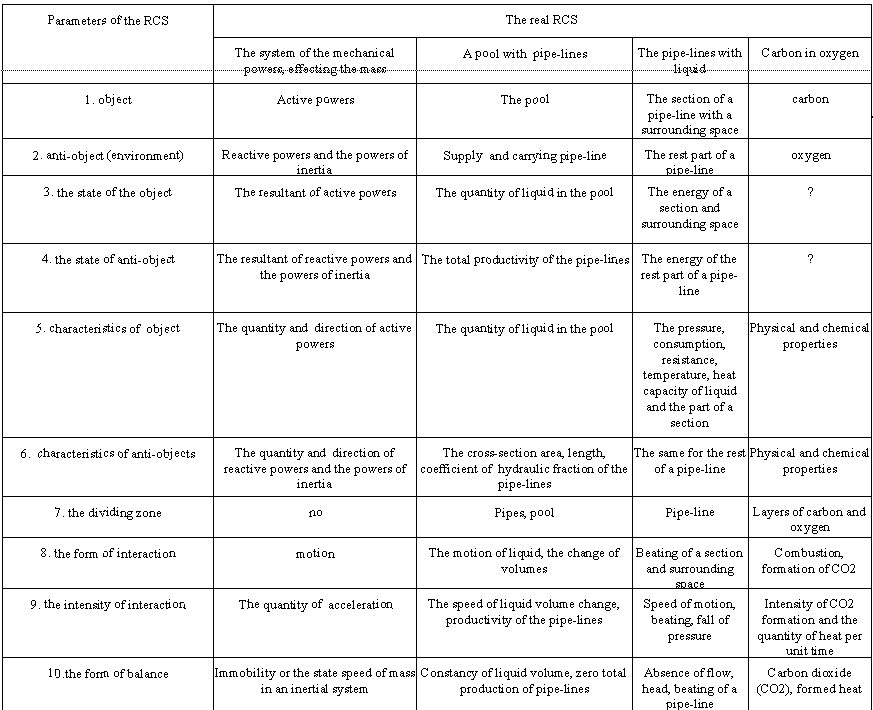
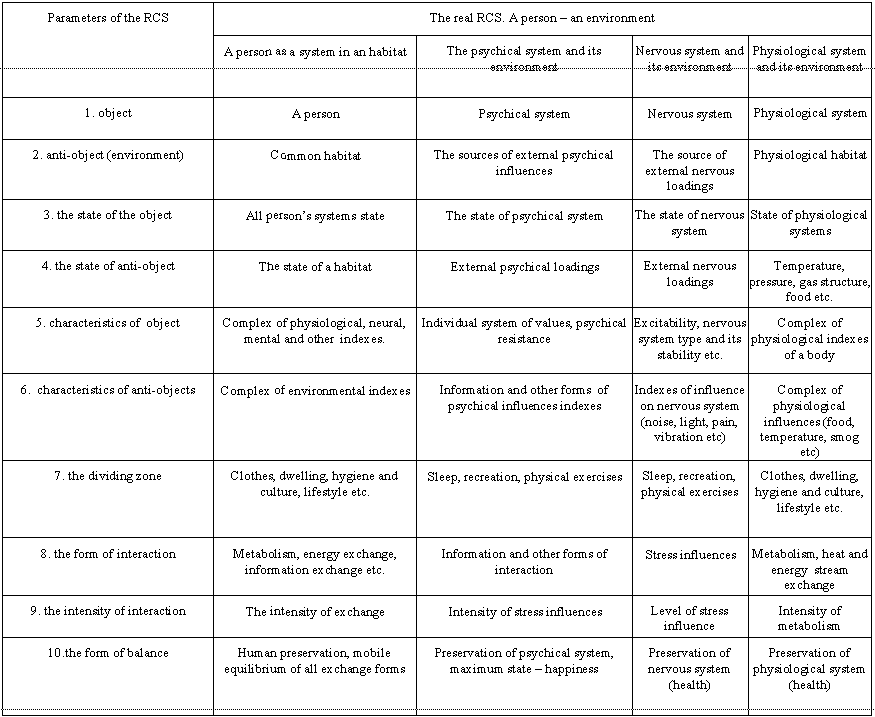
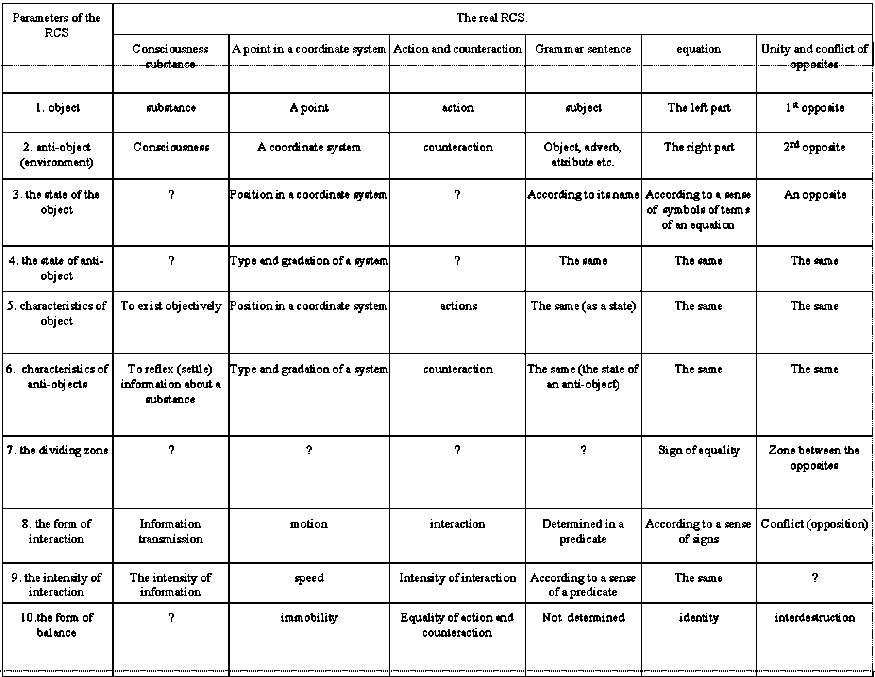
The structural and functional analyses of some of models and real CCS are shown in the table 1. The most close to the ACS are the CCS the stable balance of which is annihilation. The division “object – anti-object (the environment)” is relative (arbitrary) in many cases especially for the integral parts of the CCS. As a rule, exactly for those systems such a division was not made up historically.
Some of the examples till now have no fixed parameters (they are marked by the “?”). Most of them are in the most simple and complicated CCS. These deficiencies in the system overview mean the lack of investigations in it, as well as the possible investigation trend. For the model it could mean an imperfection. The shown systems are not neither simple nor complicated from the TCS positions, but their parameters are not described by the adopted quality and quantity indexes and the systems of measure units. The main parameters shown below are unified for any systems and objects. The methodologically depended specific parameters are defined by the object nature.
For example, balance as the final aim of the interaction is the unified parameter of any СCS. But such a variety as mobile balance of a system person-environment (with metabolism, information and energy exchange etc.) is peculiar only for this system. In the same way we can analyze a person’s subsystems of any hierarchical level, i.e. separate organs, parts of organs etc.
For the complicated compound systems, that consist of many objects, have different states (not only those in concentrated, but in distributed states (environment) as well) and those that have some of assumptions that are qualified as independent functioning factors (i.e. states), the more convenient description as an analytic one.
The analytically described concept for the cases of easy and complicated ACS and СCS is given below [53].
The easiest case of ACS as it was said above could be given in a form of two opposite parts:
Taking into account that some of the parts of an ACS are integral (objects) and the other are not (environments), we would write:
Taking into account possible levels of interaction and balances for the first level we could write:
Summing up all of the parts of an ACS on all levels and turning to a RCS we will write:
| Table 1. |
The real RCS |
The manometer tube with a liquid |
1st tube |
2nd tube |
The potential energy of the 1st tube relevant to the 2nd |
The potential energy of the 2nd tube relevant to the 1st |
Volume, density, the level of the liquid in the 1st tube |
The same for the 2nd tube |
Connecting tube |
The motion of liquid |
The speed of motion |
The equality of liquid level |
|
|
The heat body in the cold water |
The heat body |
Cold water |
The heat energy of water relevant to the water |
The heat energy of water relevant to the body |
The volume, specific heat capacity, temperature |
The same |
water |
Heat transfer |
The intensity of the heat flow |
The equality of temperatures |
|
|
The body in the environment (physical vacuum) |
The body |
Environment, physical vacuum |
The quantity of material |
The extend, density, structure of vacuum |
The mass, dimensions, charge, speed, temperature, structure, color, strength etc. |
Intensity, penetrability, the speed of wave propagation etc. |
space |
? |
? |
? |
|
|
Electron-positron |
electron |
positron |
An electron charge |
A positron charge |
The quantity of a charge, dimension, a sign of a charge, the speed of motion relatively an anti-object |
The same |
no |
? |
?? |
annihilation |
|
Parameters of the RCS |
1. object |
2. anti-object (environment) |
3. the state of the object |
4. the state of anti-object |
5. characteristics of object |
6. characteristics of anti-objects |
7. the dividing zone |
8. the form of interaction |
9. the intensity of interaction |
10.the form of balance |
| The real RCS |
Carbon in oxygen |
carbon |
oxygen |
? |
? |
Physical and chemical properties |
Physical and chemical properties |
Layers of carbon and oxygen |
Combustion, formation of CO2 |
Intensity of CO2 formation and the quantity of heat per unit time |
Carbon dioxide (CO2), formed heat |
|
The pipe-lines with liquid |
The section of a pipe-line with a surrounding space |
The rest part of a pipe-line |
The energy of a section and surrounding space |
The energy of the rest part of a pipe-line |
The pressure, consumption, resistance, temperature, heat capacity of liquid and the part of a section |
The same for the rest of a pipe-line |
Pipe-line |
Beating of a section and surrounding space |
Speed of motion, beating, fall of pressure |
Absence of flow, head, beating of a pipe-line |
|
A pool with pipe-lines |
The pool |
Supply and carrying pipe-line |
The quantity of liquid in the pool |
The total productivity of the pipe-lines |
The quantity of liquid in the pool |
The cross-section area, length, coefficient of hydraulic fraction of the pipe-lines |
Pipes, pool |
The motion of liquid, the change of volumes |
The speed of liquid volume change, productivity of the pipe-lines |
Constancy of liquid volume, zero total production of pipe-lines |
|
The system of the mechanical powers, effecting the mass |
Active powers |
Reactive powers and the powers of inertia |
The resultant of active powers |
The resultant of reactive powers and the powers of inertia |
The quantity and direction of active powers |
The quantity and direction of reactive powers and the powers of inertia |
no |
motion |
The quantity of acceleration |
Immobility or the state speed of mass in an inertial system |
| Parameters of the RCS |
1. object |
2. anti-object (environment) |
3. the state of the object |
4. the state of anti-object |
5. characteristics of object |
6. characteristics of anti-objects |
7. the dividing zone |
8. the form of interaction |
9. the intensity of interaction |
10.the form of balance |
| The real RCS. A person – an environment |
Physiological system and its environment |
Physiological system |
Physiological habitat |
State of physiological systems |
Temperature, pressure, gas structure, food etc. |
Complex of physiological indexes of a body |
Complex of physiological influences (food, temperature, smog etc) |
Clothes, dwelling, hygiene and culture, lifestyle etc. |
Metabolism, heat and energy stream exchange |
Intensity of metabolism |
Preservation of physiological system (health) |
|
Nervous system and its environment |
Nervous system |
The source of external nervous loadings |
The state of nervous system |
External nervous loadings |
Excitability, nervous system type and its stability etc. |
Indexes of influence on nervous system (noise, light, pain, vibration etc) |
Sleep, recreation, physical exercises |
Stress influences |
Level of stress influence |
Preservation of nervous system (health) |
|
The psychical system and its environment |
Psychical system |
The sources of external psychical influences |
The state of psychical system |
External psychical loadings |
Individual system of values, psychical resistance |
Information and other forms of psychical influences indexes |
Sleep, recreation, physical exercises |
Information and other forms of interaction |
Intensity of stress influences |
Preservation of psychical system, maximum state – happiness |
|
A person as a system in an habitat |
A person |
Common habitat |
All person’s systems state |
The state of a habitat |
Complex of physiological, neural, mental and other indexes. |
Complex of environmental indexes |
Clothes, dwelling, hygiene and culture, lifestyle etc. |
Metabolism, energy exchange, information exchange etc. |
The intensity of exchange |
Human preservation, mobile equilibrium of all exchange forms |
| Parameters of the RCS |
1. object |
2. anti-object (environment) |
3. the state of the object |
4. the state of anti-object |
5. characteristics of object |
6. characteristics of anti-objects |
7. the dividing zone |
8. the form of interaction |
9. the intensity of interaction |
10.the form of balance |
| The real RCS. |
Unity and conflict of opposites |
1st opposite |
2nd opposite |
An opposite |
The same |
The same |
The same |
Zone between the opposites |
Conflict (opposition) |
? |
interdestruction |
|
equation |
The left part |
The right part |
According to a sense of symbols of terms of an equation |
The same |
The same |
The same |
Sign of equality |
According to a sense of signs |
The same |
identity |
|
Grammar sentence |
subject |
Object, adverb, attribute etc. |
According to its name |
The same |
The same (as a state) |
The same (the state of an anti-object) |
? |
Determined in a predicate |
According to a sense of a predicate |
Not determined |
|
Action and counteraction |
action |
counteraction |
? |
? |
actions |
counteraction |
? |
interaction |
Intensity of interaction |
Equality of action and counteraction |
|
A point in a coordinate system |
A point |
A coordinate system |
Position in a coordinate system |
Type and gradation of a system |
Position in a coordinate system |
Type and gradation of a system |
? |
motion |
speed |
immobility |
|
Consciousness substance |
substance |
Consciousness |
? |
? |
To exist objectively |
To reflex (settle) information about a substance |
? |
Information transmission |
The intensity of information transmission |
? |
| Parameters of the RCS |
1. object |
2. anti-object (environment) |
3. the state of the object |
4. the state of anti-object |
5. characteristics of object |
6. characteristics of anti-objects |
7. the dividing zone |
8. the form of interaction |
9. the intensity of interaction |
10.the form of balance |
If we add the sum of assumptions of all levels a CCS would be transformed into an ACS:
The dependences given above are describing CS only structurally not changing parts included in it, i.e. reflect only momentary state of a CS.
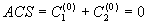 = R0,
= R0,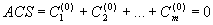 = R(0),
= R(0),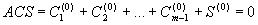 = R(0)
= R(0)
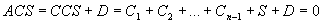 = R(0)
= R(0)
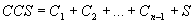 .
.
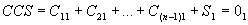 = R(0)1
= R(0)1
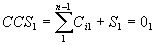 ~ R(0)1
~ R(0)1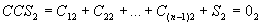 ~ R(0)2,
~ R(0)2,
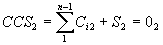 ~ R(0)2.
~ R(0)2.
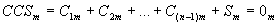 ~ R(0)m,
~ R(0)m,
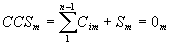 ~ R(0)m
~ R(0)m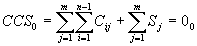
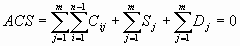 = R(0)
= R(0)